School of Design Innovation
Nestled within Mahindra University, the School of Design Innovation (SDI) is set to shape the future of design education, ushering in a paradigm shift from traditional design to design innovation. As an interdisciplinary hub, SDI seamlessly integrates with multiple schools, like Management, Entrepreneurship, Engineering, etc. fostering a holistic learning ecosystem.
Our journey began over a decade ago through a collaboration with École Centrale, where design thinking and media studies courses were introduced as compulsory courses into engineering education.
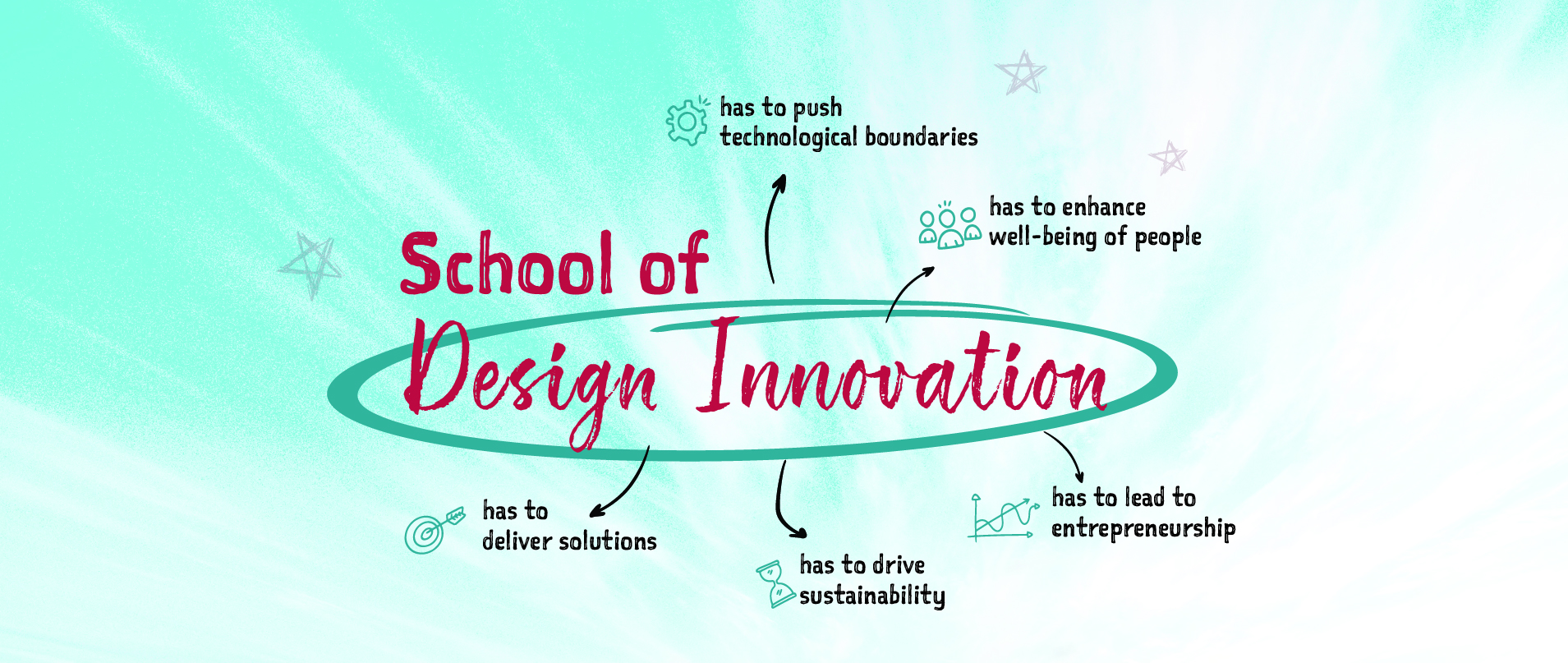
Mahindra University’s School of Design Innovation aims to foster and groom young minds to drive the future. The emphasis is on teaching Design Thinking for innovation, which is a confluence of understanding the needs of people, creative ideation, technology adoption, crafting solutions and deployment. Design Thinking is all pervasive, providing solutions in disciplines such as the arts, social sciences, law, health, engineering, business, and others. The university has well equipped labs and studios with trained staff to nurture and guide students through these learning components, which spread across disciplines, leading to Innovation.
Design Innovation finds innovative solutions to consumer needs, explores contemporary technologies, and create new businesses or solve problems in current industries. It germinates from a deep commitment to serve people for both physical and psychological needs
Mahindra University’s School of Design Innovation (SDI) offers exciting opportunities for aspiring students in the field of design with the following offerings:
Join School of Design Innovation as it embarks on this exciting journey of exploration and innovation, shaping the future of design education and making a lasting impact across industries, communities, and economies.
Mission:
The School of Design Innovation at Mahindra University is dedicated to nurturing designers to create impactful, human-centred solutions keeping in mind the local cultural practices and systems. The School’s focus is to encourage entrepreneurship and support govt. and NGOs to promote sustainable livelihoods. The School’s mission is to drive innovation that works for people, deliver real-world benefits, and inspires future-ready designers.
Through talented and motivated faculty and international collaborations SDI strives to bring in the required talents in the students through live projects. The School’s collaboration with incubators and its adaptative curriculum enables it to introduce startup culture early in the students’ learning. The school’s endeavour is to create innovative leaders who will shape industries, communities, and economies for a better world.
Vision:
Innovation can change the world in ways that are unimaginable. Yet there are some who can visualize such a change and develop product and services that are readily adopted by the people and transform the way they live and dream. Soon such innovations become the strong backbone of the society, industry, and the economy.
The School of Design Innovation at Mahindra University envisions a world where designers drive meaningful change. They solve real-world problems and create transformative solutions. SDI aims to nurture designers who not only understand people but also develop impactful products and services that address societal and industrial challenges. The goal of the School is to foster and groom such young minds to be the future-focused innovative leaders.
The School of Design Innovation will be mentored by the best design brains from across the world. This pursuit of design excellence is bolstered by a partnership with the Pininfarina Design Academy in Torino, Italy and Shenoy Innovation Studio IDC IITB.
The labs and studios across Mahindra University are well equipped so that students can build their mock-ups and proof of concepts for design innovation. The students are motivated to use the Chakku’s 7 concerns of design thinking, formulated by our founding dean Prof. B.K. Chakravarthy from his 3 decades of design innovation experience. This is used as a project management template and collaborative tool for taking design to market.
Design Differentiator:
SDI design methodology follows the Innovation by Design paradigm, where design thinking exists in a continuous, reciprocal loop like a Möbius strip- ensuring that the process and the outcomes are seamlessly interconnected and continuously refined.
Mahindra University promotes teamwork among students from various fields to tackle real-world challenges. The humanities help in understanding people’s needs, while the School of Design Innovation drives creativity through design thinking. The entrepreneurship program focuses on testing and validating ideas, and the engineering department assists in building prototypes. Together, all these departments collaborate to find effective solutions to problems.
The School of Design Innovation offers an immersive learning experience with expert-led online and offline lectures, one-on-one mentoring, and teamwork-driven projects. Enriched with field visits, cross-cultural art, and design boot camps, the program prepares students for real-world impact.
For the paradigm shift from Design to Design Innovation, the School uses the Chakku’s 7 concerns for innovation by design wherein the students are trained to learn to understand that the design needs to deliver and user delight is the key.
 1st C The Cause: The resolve to solve a problem
1st C The Cause: The resolve to solve a problem
Every design project is initiated by a need which becomes the ‘Cause’ of the entire journey that follows. This need may be a commercial requirement, a social necessity, or a specific niggling problem with an existing product. The recognition of such a need is a key trigger for the project and it can be identified by any of the stakeholders connected to the product – a product manufacturer or marketer, a user, or a product designer.
 2nd C The Context: Understanding the problem space and the environment
2nd C The Context: Understanding the problem space and the environment
To study and understand an existing product or similar products in the market, it is critical that the environment in which the product is used is understood comprehensively. This means that a designer must study the users and their perspectives on the product. Often this involves several rounds of interaction and observation.
 3rd C The Comprehension: Arriving at design insights
3rd C The Comprehension: Arriving at design insights
At this stage, the designer analyses all the information gathered and methodically lists out their observations and perceptions of any notable issues in the use of the product. Such analysis results in the thorough, all-round comprehension of a product as it functions within the contexts of its use. The design insights thus arrived at give rise to creative ideas and form the basis for the intervention that follows.
 4th C The Check: Creating a project brief
4th C The Check: Creating a project brief
The check is an essential step in understanding what requirements the product should ultimately meet and what problems the design intervention should address. The check, which is often a document in the form of a product brief, is created from the design insights and must be approved by the client. The product brief is an important point of reference throughout the journey as concepts and prototypes are created and evaluated.

5th C The Conception: Generating ideas and concept
Using the product brief, the designer arrives at multiple ideas to come up with solutions for the problems listed. At this crucial stage, ideas are proposed and grouped into clusters. This makes possible the consideration of multiple concepts. Finally, the team zeroes in on one all-encompassing concept that best addresses all aspects of the product.
 6th C The Crafting: Building mock-ups and prototypes
6th C The Crafting: Building mock-ups and prototypes
The final concept is further refined against various criteria like use of material and manufacturing limitations. Depending on the user profile, the designer at this stage creates several style options and zeroes in on the one that addresses the aesthetics concerns in the best manner. The final product design is showcased by creating small scale mock-up models, CAD models or working prototypes. The final product which meets the product brief conditions is then taken up for mass production.
 7th C The Connection: Delighting the user
7th C The Connection: Delighting the user
The last but critically important concern is the connection the new product makes with the user. This connection or the bond between the user and the product is formed only when the user is satisfied with the product’s performance and begins to cherish it, which in turn creates an increased demand for the product. In fact, it is the customer’s satisfaction that makes a winning product and functions as the most important criterion for innovation.
The department offers 4 disciplines -Industrial Design, Communication Design, Interaction Design and Apparel Design. Depending on the electives and projects and internships the students choose, their area of interest evolves. This is the focus of design innovation where SDI wants to see projects coming to life.
Interaction Design:
Present State/Challenges: Interaction design struggles with balancing usability, inclusivity, and the ethical use of AI-driven interfaces. Many experiences lack true personalization and emotional intelligence.
Future Direction: The future of interaction design will focus on adaptive, AI-enhanced user experiences, gesture-based interfaces, and neuro design (using brain-computer interfaces for seamless interactions). Ethical and human-centred AI will ensure technology serves people intuitively and inclusively.
- User Interface (UI) Design – Designing intuitive digital interfaces and user flows.
- User Experience (UX) – Designing intuitive, inclusive, and seamless user experiences
- Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) – Researching how people interact with digital and physical systems.
- Extended Reality (XR) Design – Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR) experiences.
- Game Design and Games Studies – Coding, development, design, study, level design, character creation of games.
- Wearable & Smart Device Interaction – Designing interactions for smartwatches, fitness trackers, and AR glasses.
- Service Design & Systems Thinking – Mapping user journeys and designing holistic service ecosystems.
- Gamification & Interactive Storytelling – Designing engagement-driven experiences in apps and products.
- Automotive & Transportation UX – Human-cantered interfaces for vehicles and mobility solutions.
- Accessibility & Inclusive Design – Designing for diverse abilities, neurodivergence, and universal usability.
Communication Design:
Present State/Challenges: Communication design faces challenges in information overload, digital saturation, and shrinking attention spans. Designers must create content that is both visually compelling and easily digestible.
Future Direction: The future of communication design will be shaped by AI-generated content, immersive storytelling (AR/VR), and personalized, data-driven visual communication. Ethical design, accessibility, and inclusivity will play key roles in shaping the next era of media and branding.
- Graphic Design: Focuses on visual content creation for print and digital media, including logos, brochures, posters, and websites.
- Branding and Identity Design: Involves creating a cohesive visual and thematic identity for businesses or products, including logos, colour schemes, and overall brand guidelines.
- Motion Graphics Design: Involves creating animated visual content for use in videos, presentations, websites, and other digital platforms.
- VFX: Create realistic or stylized imagery by integrating computer-generated elements with live-action footage, covering skills such as compositing, 3D animation, tracking, and simulation techniques.
- Advertising Design: Focuses on creating visual content for advertisements across various media, including print, digital, and outdoor advertising.
- Illustration: Involves creating original artwork for use in books, magazines, advertisements, and digital media to visually convey messages or stories.
- Information Design: Specializes in presenting complex data and information in a clear and understandable manner, often through infographics, charts, and diagrams.
- Film and Video Design: Courses and subjects in Film and Video Design by design schools typically cover storytelling, cinematography, scriptwriting, editing, sound design, motion graphics, visual effects (VFX), animation, and media production.
- Animation Design: Create compelling visual stories by mastering principles of motion, character development, and industry-standard digital tools.
- Social Media design: Understanding new digital tools and its application in social media.
Industrial Design
Present State/Challenges: Industrial design is evolving with a strong focus on sustainability, user-centric innovation, and material efficiency. Challenges include overproduction, environmental impact, and the need for circular economy practices.
Future Direction: The future of industrial design lies in biodegradable materials, AI-driven optimization, and modular product design. Human-centred innovation, powered by IoT and smart manufacturing, will create adaptable, sustainable, and personalized products.
- Product Design: Involves designing consumer products, from electronics and household items to furniture and appliances, focusing on usability, aesthetics, and manufacturability.
- Transportation Design: Centers on designing mobility solution such as cars, motorcycles, bicycles, trains, water transport and air transport, emphasizing both function and style, as well as a systems design approach
- Furniture Design: Specializes in designing functional and aesthetically pleasing furniture for residential, commercial, and public spaces.
- Packaging Design: Focuses on creating packaging solutions that are not only visually appealing but also functional, sustainable, and protective of the contents.
- Exhibition Design: Involves designing displays and fixtures for exhibitions, trade shows, museums, and retail spaces to enhance the presentation and interaction of products or artifacts.
- Medical Device Design: Specializes in designing medical and healthcare products, ensuring they are user-friendly, safe, and effective for both patients and healthcare providers.
- Lighting Design: Focuses on designing lighting products and systems that provide effective illumination while also considering aesthetics, energy efficiency, and user comfort.
- Toy and Game Design: Involves creating toys and games that are not only entertaining but also safe, educational, and suitable for their intended age group.
- Sustainable Design: Emphasizes on designing products with a focus on environmental sustainability, including using eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient processes, and promoting product longevity and recyclability.
- Ergonomic Design: Specializes in designing products that optimize human well-being and overall system performance, ensuring that products are comfortable, efficient, and safe to use.
Apparel Design
Present State/Challenges:
The apparel industry faces challenges in sustainability, fast fashion waste, and ethical production, as rapid consumer demand pressures brands to compromise on environmental and social responsibility.
Future Direction:
The future of apparel design is moving towards circular fashion, where AI-driven customization, biodegradable materials, and 3D-printed garments will redefine sustainability, reducing waste and promoting ethical production.
- Fashion & Textile Design – Garment and fabric innovation, aesthetics, and creative expression.
- Pattern Making & Garment Construction – Technical skills for translating designs into wearable products.
- Digital & Smart Wearables – AI-driven fashion, 3D designs, and technology-integrated clothing.
- Sustainable & Circular Fashion – Eco-friendly materials, zero-waste design, and ethical production.
- Sportswear & Functional Apparel – Performance-driven clothing for athletics, workwear, and extreme environments.
- Luxury, Couture & Ethnic Wear – High-end craftsmanship, traditional textiles, and cultural fashion.
- Fashion Business & Branding – Retail, merchandising, marketing, and entrepreneurship in apparel.
- Trend Forecasting & Consumer Behaviour – Predicting future trends using data, AI, and market insights.
- Adaptive & Inclusive Design – Clothing for diverse body types, disabilities, and gender-neutral fashion.
- Costume & Experimental Fashion – Film, theatre, avant-garde, and conceptual fashion exploration.
Innovation can change the world in ways that are unimaginable. However, there are individuals who possess the ability to envision these transformations and create innovative designs that can be easily embraced by individuals, ultimately reshaping their lifestyles and aspirations. Soon such Design innovations become the backbone of the society, industry, and the economy.
Mahindra University’s School of Design Innovation aims to foster and groom young minds to drive the future. The emphasis is on teaching Design Thinking for innovation which is a confluence of understanding the needs of the people, creative ideation, technology adoption, crafting solutions and deployment. Design Thinking is all pervading, providing solutions in disciplines such as arts, social sciences, law, health, engineering, business, and other fields.
We have well equipped Centers, labs and Studios with trained staff to nurture and guide students through these learning components leading to Innovation.
Design Innovation finds innovative solutions to consumer needs, explore good technologies, and create new businesses or solve organizational challenges.
Design Innovation germinates from a deep commitment to serve people for both physical and psychological needs.
The Chakku’s 7C’s methodology focuses on the key concerns a designer should develop throughout all phases of design innovation.
The 7 concerns of Design thinking for innovation or the Chakku’s 7Cs for design Innovation are:

Dr. B. K. Chakravarthy
School of Design Innovation
Dr. B. K. Chakravarthy is a renowned educator and innovator who brings a wealth of expertise and knowledge to his role as the Founding Dean at Mahindra University’s School of Design Innovation, following his tenure as a Professor at the IDC School of Design, IIT Bombay. Dr. Chakravarthy has a strong foundation in both academics and business. His teaching methodology emphasizes the practical application of information, which is demonstrated by the way he incorporates sponsored projects and real-world case studies into his curricula.
Programs Offered
Recognizing design’s evolving role, Mahindra University’s School of Design Innovation crafts a dynamic, interdisciplinary approach. It blends design thinking with technology, business, and social awareness, preparing students to innovate across diverse fields and address future challenges
DESIGN – INNOVATE – PROTOTYPE – ENTREPRENUER
The School of Design Innovation will be mentored by the best design brains in India. Its labs and studios will be well equipped for conceptualization, evaluative testing, and prototyping. The CAD Studios already exist running a variety of software suitable both for product design and UX/UI.
The following laboratories will be set up:
Human Behavioral Studies Lab – which would use eye tracking, galvanic skin response, analyses of facial expression, EEG, and ergonomic studies;
Prototyping Studios – for fabricating soft materials as well as making working models. Styling studio suitable for automotive design;
The learning environment is interactive and collaborative. Additionally, there will be field visits and cross-cultural art, and design boot camps.
Further, seven concerns [7-Cs] on design thinking for innovation as elucidated by IIT Bombay will be followed to achieve meaningful design and user-centric innovations, namely:
In Fall 2024, Mahindra University is launching School of Design Innovation with the Bachelor Program in Design to start with. Soon after we will launch design programs at the Masters and Doctoral levels.
Welcome to the School of Design Innovation of Mahindra University where creativity manifests, blossoms and bear fruits.
Faculty
The School of Design Innovation will be mentored by the best design brains from across the world. This pursuit of design excellence is bolstered by a partnership with the Pininfarina design academy in Torino, Italy.
The studios across Mahindra University are well equipped to address all concerns of design innovation. The 7 concerns of design thinking are employed as project management template and collaborative tool to work across disciples for innovation.
The Mahindra University School of Design Innovation cultivates an interactive and collaborative learning environment. Students will learn from esteemed professors through both online and offline and one on one project mentoring. Students will be taught to work collaboratively in teams from the first year onwards. Additionally, the program will be enriched with field visits, cross-cultural art, and design boot camps across all the semesters.
The B.Des , M.Des and Ph.D. programs from August 15th 2024
Welcome to the School of Design Innovation at Mahindra University where creativity manifests, blossoms and bear fruits.





















